
Southern Yellow Pine(SYP) Characteristics
The sapwood of pine is a yellowish white, while the heartwood is a reddish brown, orange, or yellow heartwood.
The sapwood is usually wide in second growth stands. Heartwood begins to form when the tree is about 20 years
old. In old, slow-growth trees, sapwood may be only 1 to 2 inches in width.
All the southern pines have moderately large shrinkage but are stable when properly seasoned. The heartwood is
rated as moderate to low in resistance to decay. The sapwood is more easily impregnated with preservatives.
Physical Properties
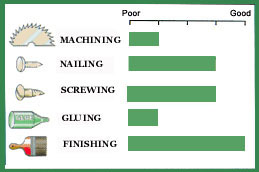
The lumber of loblolly pine is very heavy and strong, very stiff, hard and moderately high in shock resistance. It also has a straight grain, medium texture and is difficult to work with hand tools. It ranks high in nail holding capacity, but there may be difficulty in gluing. All the southern pines have moderately large shrinkage but are stable when properly seasoned. The heartwood is rated as moderate to low in resistance to decay. The sapwood is more easily impregnated with preservatives.
Main uses
The denser and higher strength southern pine is used extensively in construction of factories, warehouses, bridges, trestles, and docks in the form of stringers, and for roof trusses, beams, posts, joists, and piles. Lumber of lower density and strength finds many uses for building material, such as interior finish, sheathing, subflooring, joists, for boxes, pallets, and crates. Southern pine is also used also for tight and slack cooperage. When used for railroad crossties, piles, poles and mine timbers, it is usually treated with preservatives. The manufacture of structural grade plywood from southern pine has become a major wood-using industry.
Working Properties
Difficult to work with hand tools. It ranks high in nail holding capacity, but there may be difficulty in gluing.
@2016 Copyright by NAEC Lumber Power by NAEC. | Home | Contact Us | Phyto | Packaging List | Ash | Cherry | Hickory | Hard Maple | Soft Maple | Red Oak | White Oak | Walnut | Elm | SYP | Cypress |
